This ongoing clinical study assesses the comparability between RetinaLogik’s portable VR-based perimetry device (RVF100) and the gold-standard Humphrey Visual Field Analyzer (HFA) for glaucoma suspect evaluations.
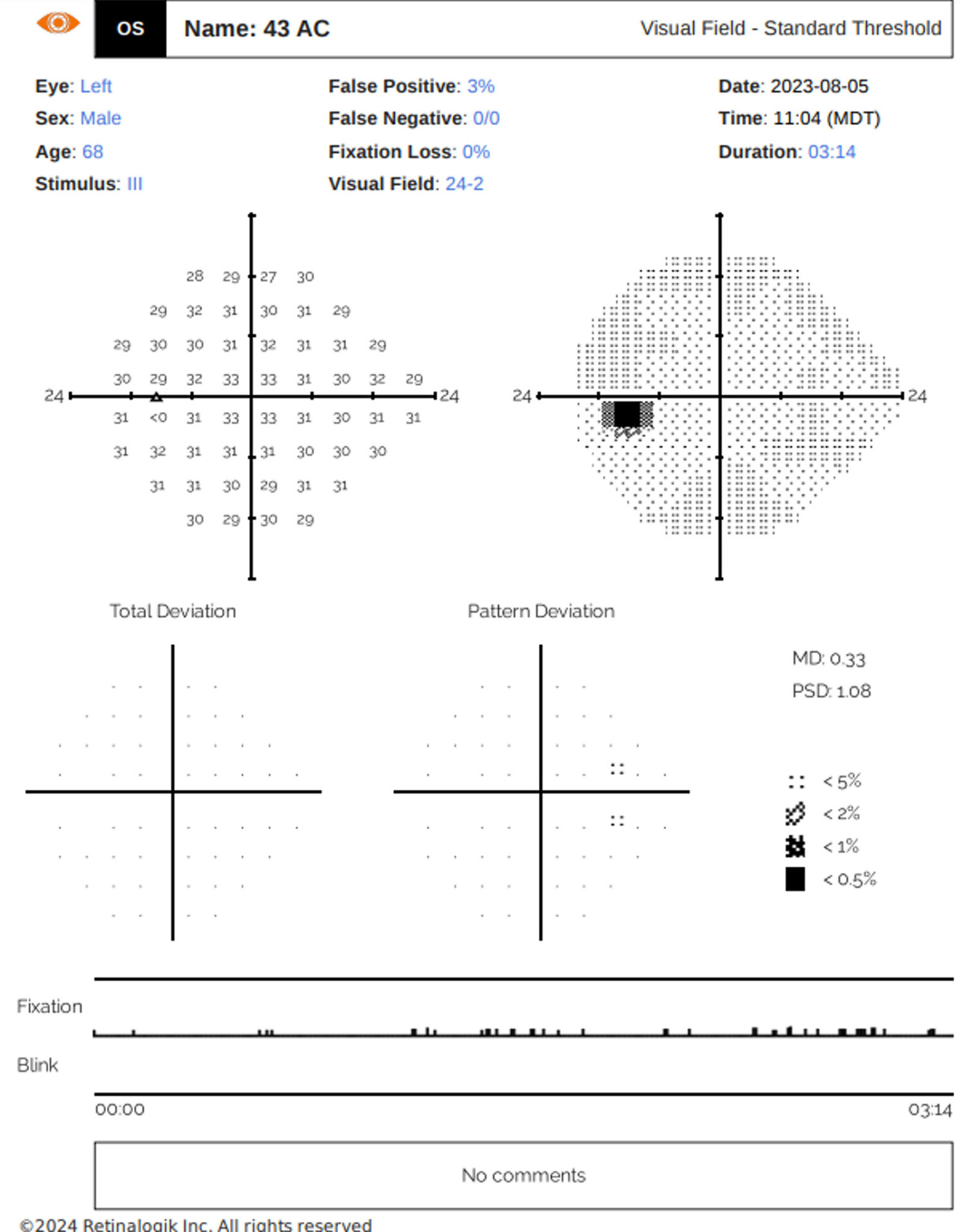
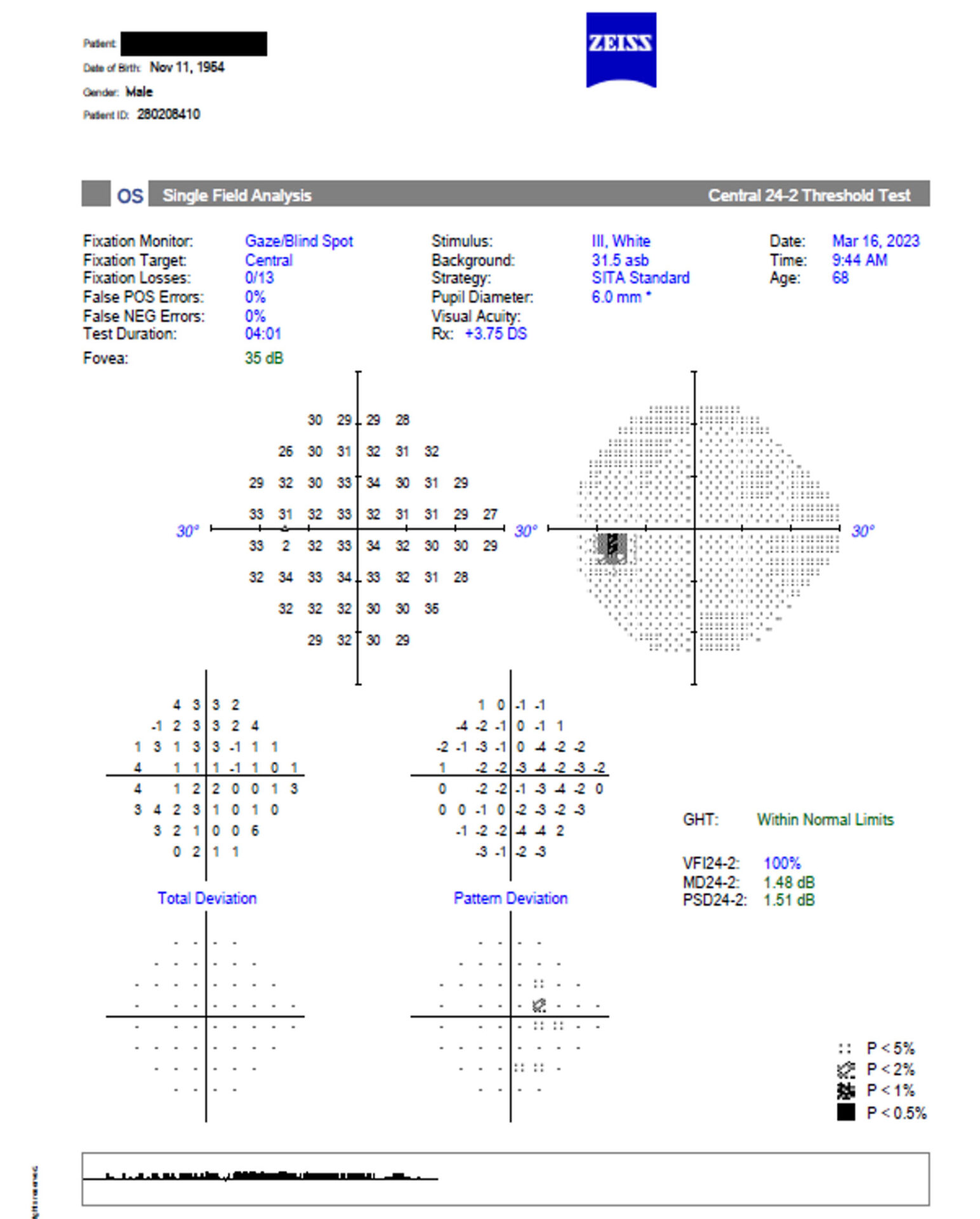
In a cohort of 18 glaucoma suspect patients (32 eyes, Media Age was 62.9), the study employed matched testing using 24-2 and 30-2 grids on both devices within a 1-month interval. The study evaluated global mean sensitivity (MS), mean deviation (MD), pattern standard deviation (PSD), and pointwise sensitivity differences.
Key Findings
- Strong correlation observed between devices:
- MD: r = 0.7677 (P < 0.0001)
- PSD: r = 0.9065 (P < 0.0001)
- Global MS: r = 0.7947 ( p < 0.001)
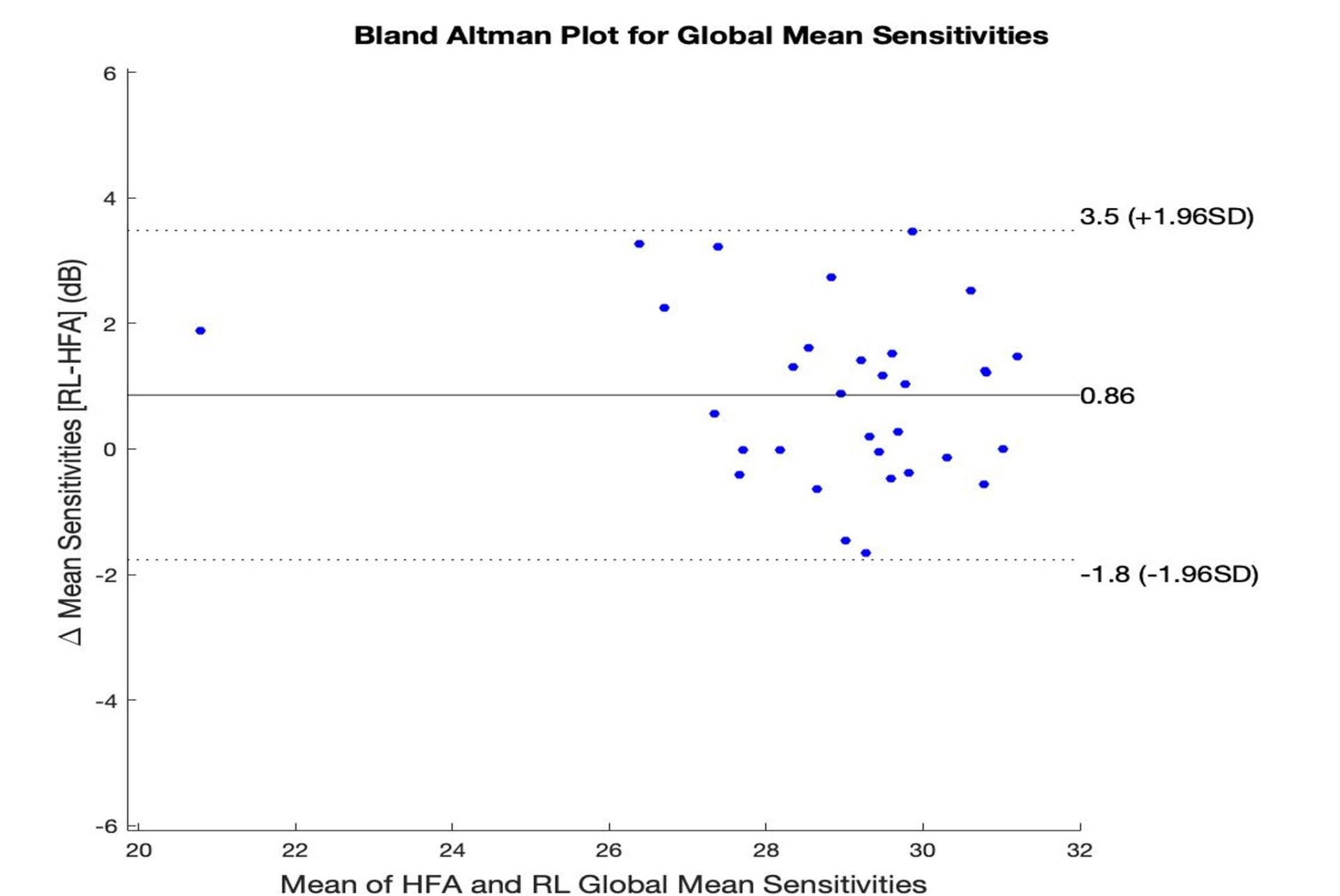
- Bland-Altman analysis showed a bias of 0.86 dB with 95% limits of agreement from -1.8 to 3.35. when comparing the MS of the VR device with HFA.
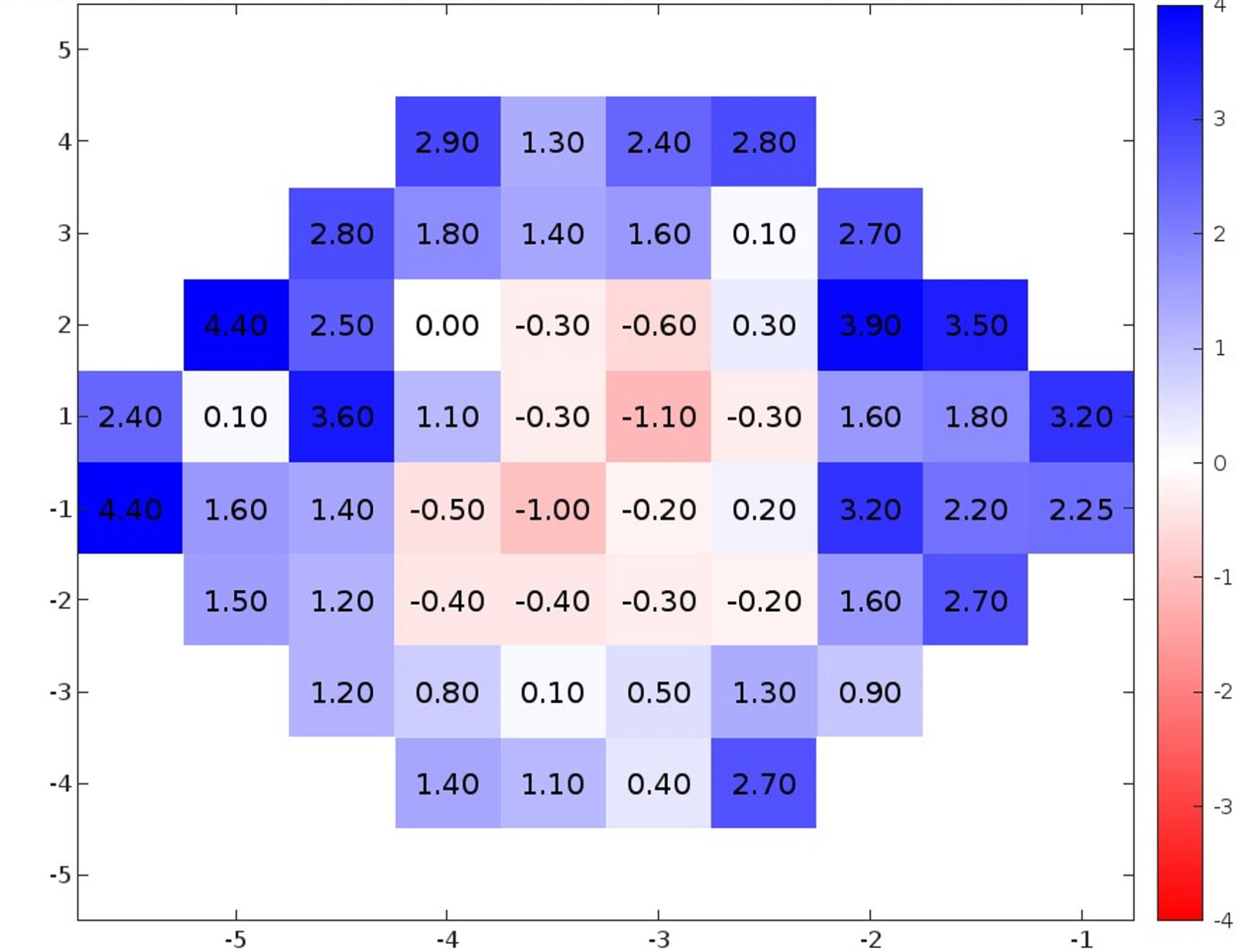
- Pointwise decibel sensitivity differences in decibel attenuation between the two devices, averaged at each stimulus location, ranged from –1.62 to 4.05 dB, with an average variation of 1.08 dB.
Conclusion
Preliminary results show strong agreement between the VR device and the HFA, suggesting non-inferiority of the VR solution. The study supports VR as a practical, cost-effective, and portable perimetry, with further research ongoing across diverse populations and clinical contexts.